Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
Problem Statement - link #
There are n cities connected by some number of flights. You are given an array flights where flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] indicates that there is a flight from city fromi to city toi with cost pricei.
You are also given three integers src, dst, and k, return the cheapest price from src to dst with at most k stops. If there is no such route, return -1
Examples #
Example 1:
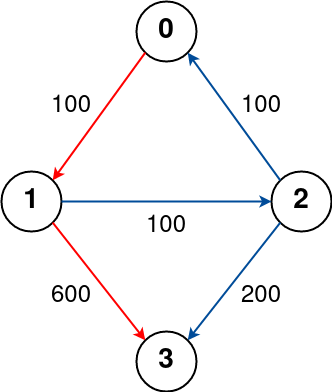
Input: n = 4, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[2,0,100],[1,3,600],[2,3,200]], src = 0, dst = 3, k = 1
Output: 700
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 3 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 600 = 700.
Note that the path through cities [0,1,2,3] is cheaper but is invalid because it uses 2 stops.
Example 2:
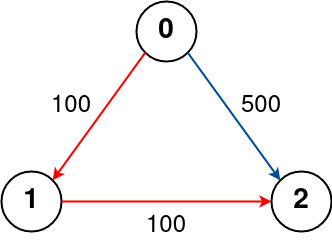
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1
Output: 200
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 100 = 200.
Example 3: 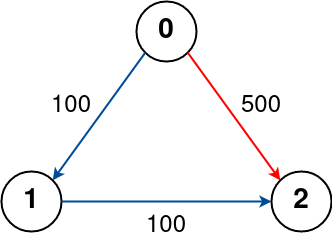
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0
Output: 500
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with no stops from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 500.
Constraints #
1 <= n <= 1000 <= flights.length <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)flights[i].length == 30 <= fromi, toi < nfromi != toi1 <= pricei <= 10^4- There will not be any multiple flights between two cities.
0 <= src, dst, k < nsrc != dst
Solutions #
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
vector<pair<int, int>> vec[n];
// array of edges with pair of dest_city and dest_price
for(auto f: flights) {
vec[f.at(0)].push_back({f.at(1), f.at(2)});
}
queue<pair<int, pair<int, int>>> q;
// current_city, current_stops, current_price
q.push({src, {0, 0}});
// dis vector for storing min cost with atmost k stops
vector<int> dis(n,1e7); dis.at(src)=0;
// BFS approach
while(!q.empty()) {
auto c = q.front(); q.pop();
int to = c.first; // current Node
int ck = c.second.first; // stops till now
int cp = c.second.second; // cost of the joruney till now
if(ck > k) continue; // if stops exceeds k then we ignore this Node
for(auto next: vec[to]) {
int nto = next.first; // next Node
int np = next.second; // cost of journey form cur to next node
if( cp+np < dis[nto]) { // checking if current total cost is than previous total cost
dis[nto] = cp+np;
q.push({nto, {ck+1, dis[nto]}});
}
}
}
if(dis[dst]==1e7) return -1; // No valid journey with given data
return dis[dst];
}
};