Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List
Problem Statement - link #
You are given a doubly linked list which in addition to the next and previous pointers, it could have a child pointer, which may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure, as shown in the example below.
Flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. You are given the head of the first level of the list.
Examples #
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12]
Output: [1,2,3,7,8,11,12,9,10,4,5,6]
Explanation:
The multilevel linked list in the input is as follows:
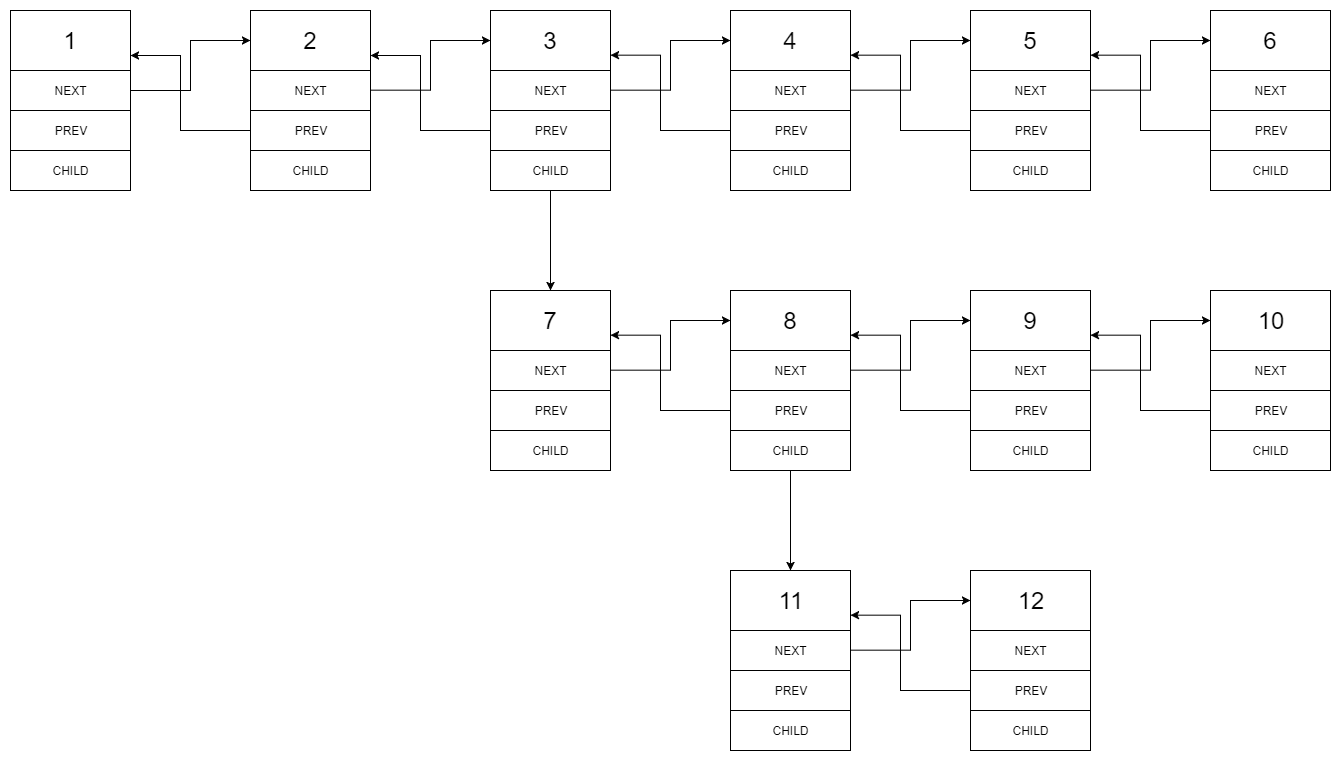
After flattening the multilevel linked list it becomes:

Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,null,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Explanation:
The input multilevel linked list is as follows:
1---2---NULL
|
3---NULL
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
How multilevel linked list is represented in test case:
We use the multilevel linked list from Example 1 above:
1---2---3---4---5---6--NULL
|
7---8---9---10--NULL
|
11--12--NULL
The serialization of each level is as follows:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null]
[7,8,9,10,null]
[11,12,null]
To serialize all levels together we will add nulls in each level to signify no node connects to the upper node of the previous level. The serialization becomes:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null]
[null,null,7,8,9,10,null]
[null,11,12,null]
Merging the serialization of each level and removing trailing nulls we obtain:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12]
Constraints #
- The number of Nodes will not exceed
1000. 1 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Solutions #
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
Node* child;
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* flatten(Node* head) {
Node* tmp = head;
vector<Node*> nodes;
int level = 1;
if(!head) return head;
while(1){
if(tmp->child != NULL)
nodes.push_back(tmp);
if(tmp->next == NULL)
if(level <= nodes.size()){
tmp = nodes[nodes.size()-1]->child;
level++;
}
else
break;
else
tmp = tmp->next;
cout<<tmp->val<<endl;
}
for(int i = nodes.size()-1; i>=0; i--){
Node* r = nodes[i]->next;
Node* c = nodes[i]->child;
nodes[i]->child = NULL;
nodes[i]->next = c;
c->prev = nodes[i];
while(c->next != NULL) c = c->next;
c->next = r;
(r!=NULL ? r->prev = c : r);
}
return head;
}
};